

Different configuration commands are used to define numbered and named ACLs. All ACLs, whether standard or extended, must be identified by a number or name. If you intend to filter on anything other than the source address, an extended ACL is necessary.
A standard ACL can filter only on the source address. All ACLs fall into one of two categories: standard or extended. Such control can restrict access of users and hosts to parts of the network, and provides a certain degree of security. Introduction to ACLsĪccess control lists perform packet filtering to control which packets can reach which area of the network.
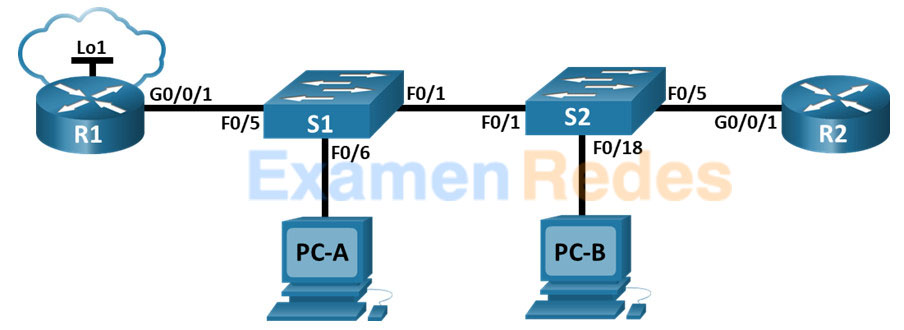
ACL LAB VERIFICATION
You may also refer to GNS3 Labs for CCNA: DHCP Server Configuration and Verification if you need help setting up hosts in GNS3, even if you are not interested in DHCP. We assume you already have GNS3 installed but you may refer to GNS3 Labs for CCNA: Getting Started if you need help setting up GNS3.

ACL LAB FREE
The article is part of the GNS3 Labs for CCNA series, and just like other pieces in the series, we provide GNS3 topology and initial configuration files as a free download. In this article, we provide a quick introduction to ACLs before moving on to their configuration and verification. However, CCNA exams tend to focus on the most common use of ACLs as traffic filters. You can do quite a few things with packets matched by ACLs. An access control list (ACL) is a sequence of conditions or statements that can match packets moving through the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
